Chapter02
变量+“+”+数据类型+编码+数据类型转换
1.变(变化)量(值)
变量=变量名+值+数据类型
变量是程序的基本组成单位
- 声明变量 int a;
- 赋值 a = 60;
int double char String
变量先声明,后使用
2. +
- 当左右两边都是数值型时,则做加法运算
- 当左右两边有一方为字符串,则做拼接运算
- 从左到右运算
3.数据类型
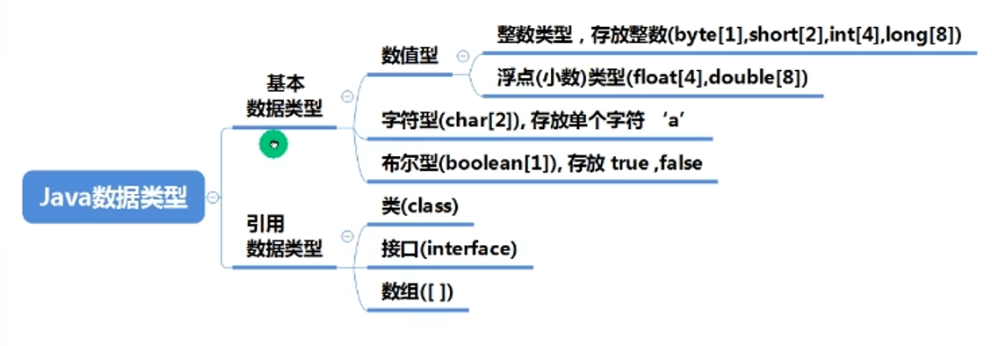
java的整型常量(具体值)默认为int型,声明long型常量须后加l或L
bit:计算机中的最小存储单位。
byte:计算机中基本存储单元,字节 1byte=8bit。
1.浮点
| 单精度float | 4字节 |
|---|---|
| 双精度double | 8字节 |
浮点数=符号位+指数位+尾数位
Java的浮点型常量(具体值)默认为double型,声明float型常量,须后加f或‘F’
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//浮点数陷阱
double num1 = 2.7;
double num2 = 8.1/3;
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(num2);
//2.7
//2.6999999999999997
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//应该是以两个数的差值的绝对值在某个精度范围内判断
错误的
if (num1 == num2){
System.out.println("相等");
}
正确的
System.out.println("相等" + Math.abs(num1 - num2));
2.字符类型
字符常量用’’单引号 字符串用””双引号
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = '\t';
char c3 = '韩';
char c4 = 97;
char c5 = 'b';
System.out.println(c1 + "\n" + c2 + "\n" + c3 + "\n" + c4 );
//输出b对应的数字
System.out.println((int)c5); //98
1
System.out.println('a' + 10); //107
3.布尔类型
java不可以用0或非0的整数代替false或true
4.基本数据类型转换
自动类型转换
精度小的类型自动转换为精度大的数据类型
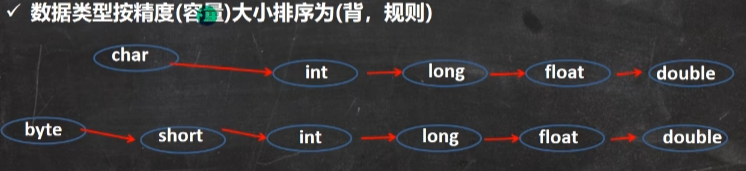
把精度(容量)大的数据类型赋值给精度(容量)小的数据类型时,就会报错,反之就会进行自动类型转换.
- byte,short,char三者可以计算,在计算时首先转换为int类型。
1
2
3
4
5
byte b2 = 1;
short s1 = 1;
short s2 = b2 + s1;
错误,b2 + s1 运算之后,为int类型,不能赋值给short
即使是同类型(相同或混合)也不行
- boolean 不参与类型的自动转换
- 自动提升原则:表达式结果的类型自动提升为操作数中最大的类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
byte b1 = 1;
short b2 = 100;
int b3 = 200;
double b4 = 1.1;
double sum = b1 + b2 + b3 + b4;
强制类型转换
会损失数据精度
1
2
3
int n1 = (int)1.9;
System.out.println(n1);
结果为1
数据溢出
1
2
3
4
int j = 2000;
byte c1 = (byte)j;
System.out.println(c1);
结果为-48,而不是2000
数据从 精度 大→ 小 ,需要强制转换
强转符号只针对于最近的操作数有效
1
2
3
4
5
int x =(int)10*3.5+6*1.5;
编译错误,只是把10转换成了int类型,与3.5相乘,
变成double类型,无法赋值给int
正确做法,用小括号提升优先级
int x = (int)(10*3.5+6*1.5);
char类型可以保存int的常量值,但不能保存int的变量值,需要强转
1
2
3
4
char c1 = 100; ok
int m =100; ok
char c2 = m; 错误
char c3 = (char)m;
练习
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
判断是否能够通过编译
1. short s = 12; //ok
s=s-9;//错误int->short
2. byte b = 10; //ok
b =b +11;//错误int->byte
b =(byte)(b+11); //正确,使用强转
3.char c = 'a'; //ok
int i = 16; //ok
float d = .314F; //ok
double result = c + i + d; //ok float->double
4. byte b = 16; //ok
short s = 14: //ok
short t = s+b;1/错误
基本数据类型和String类型的转换
基本类型→字符串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
int n1 = 100;
float f1 = 1.1F;
double d1 = 4.5;
boolean b1 = true;
String s1 = n1 + "";
String s2 = f1 + "";
String s3 = d1 + "";
String s4 = b1 + "";
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
字符串→基本类型 需要用到包装类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
String s5 = "123";
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(s5);
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(s5);
float num3 = Float.parseFloat(s5);
long num4 = Long.parseLong(s5);
byte num5 = Byte.parseByte(s5);
boolean num6 = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
short num7 = Short.parseShort(s5);
System.out.println("num1: " + num1);
System.out.println("num2: " + num2);
System.out.println("num3: " + num3);
System.out.println("num4: " + num4);
System.out.println("num5: " + num5);
System.out.println("num6: " + num6);
System.out.println("num7: " + num7);
把字符串转成字符char -> 取字符串的第一个字符
1
2
//字符串转字符,取
System.out.println(s5.charAt(0));
在将String类型转成基本数据类型时,要确保String类型能够转成有效的数据,可以把“123”,转成一个整数,但是不能把“hello”转成一个整数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
char c1 ='男';
char c2 = '女';
System.out.println(c1 +c2);
//得到男字符码值+女 字符码值